| 宜城教育365速发国际靠谱么_365bet亚洲官方网址_预付365商城下载网www.bjtlcd.com 主动表被动的若干情形
1. 连系动词(如look, sound, smell, feel, taste, prove等)要用主动表被动,因为连系动词为不及物动词,它们没有被动语态形式。如:
The building looks very beautiful. 这座建筑看上去很美。
Your idea proved to be wrong. 你的想法证实是错的。
2. 当open, close, shut, lock, move, read, wash, clean, cook, cut, wear, carry 等用作不及物动词且表示主语的某种属性时,通常用主动形式表示被动意义:
The door won’t shut. 这门关不上。
The book sells quickly. 这书销售得快。
3. 有的动词本身含有被动意味,通常用主动形式来表示被动含义。如:
Her coat caught on the nail. 她的大衣被钉子钩住了。
Her eyes filled with tears. 她眼睛里充满了眼泪。
4. 不定式to blame, to let 用作表语时,通常要用主动表被动。如:
Who is to blame? 该怪谁呢?
The house is to let. 此屋出租。
5. 某些“be+形容词+to do”结构中的不定式通常要用主动形式表示被动意义。如:
The book is difficult to understand. 这书很难懂。
The music isn’t pleasant to listen to. 这音乐不好听。
The picture is interesting to look at. 这幅画看起来挺有趣的。
注:这类结构的特点是句子主语就是其后不定式的逻辑宾语,按理说其中的不定式要用被动形式,但习惯上却要用主动表被动。这类形容词常见的有convenient, dangerous, difficult, easy, hard, impossible, interesting, nice, pleasant, safe, tough, tricky, unpleasant 等。
6. 不定式用于某些动词(如have, have got, get, want, need等)的宾语后作定语时,如果不定式的逻辑主语就是句子的主语,通常用主动形式表示被动意义。如:
Do you have time to help us? 你有时间帮助我们吗?
I have some clothes to wash. 我有一些衣服要洗。
I want something to drink. 我想喝点什么。
注:若不定式的逻辑主语不是句子的主语,则应用被动式,比较:
I have something to type. 我有些东西要打(字)。(指自己打字)
I have something to be typed. 我有些东西要打(字)。(指请人打字)
7. 在 too…to do sth 和…enough to do sth这两个结构中,若句子主语与其后不定式为to do sth被动关系,则该不定式通常用主动形式表示被动意义(有时也可直接用被动式)。如:
The writing is too faint to read. 这笔迹太模糊,看不清。
These boxes are not strong enough to use [to be used] as a platform. 这些箱子不够牢,不能用作站台。
8. be worth后的动名词要用主动表被动。如:
This movie is worth seeing. 这部影片值得一看。
She’s not worth getting angry with. 犯不上跟她生气。
注:与worth相似的worthy却不一样,其后不接动名词而接不定式(若接动名词则其前应有介词of),且要用被动式表示被动含义:
This book is worthy to be read [of being read]. 这本书值得一读。
9. 在need, want, require等少数表示“需要”的动词后的动名词用主动形式表被动意义。如:
The house needs cleaning. 房子需要打扫了。
These children require looking after. 这些孩子需要照看。
This wall requires repairing. 这面墙需要修理了。
注:该结构中的动名词改用不定式则要用被动式表被动。如:
The house needs to be cleaned. 房子需要打扫了。
These children require to be looked after. 这些孩子需要照看。
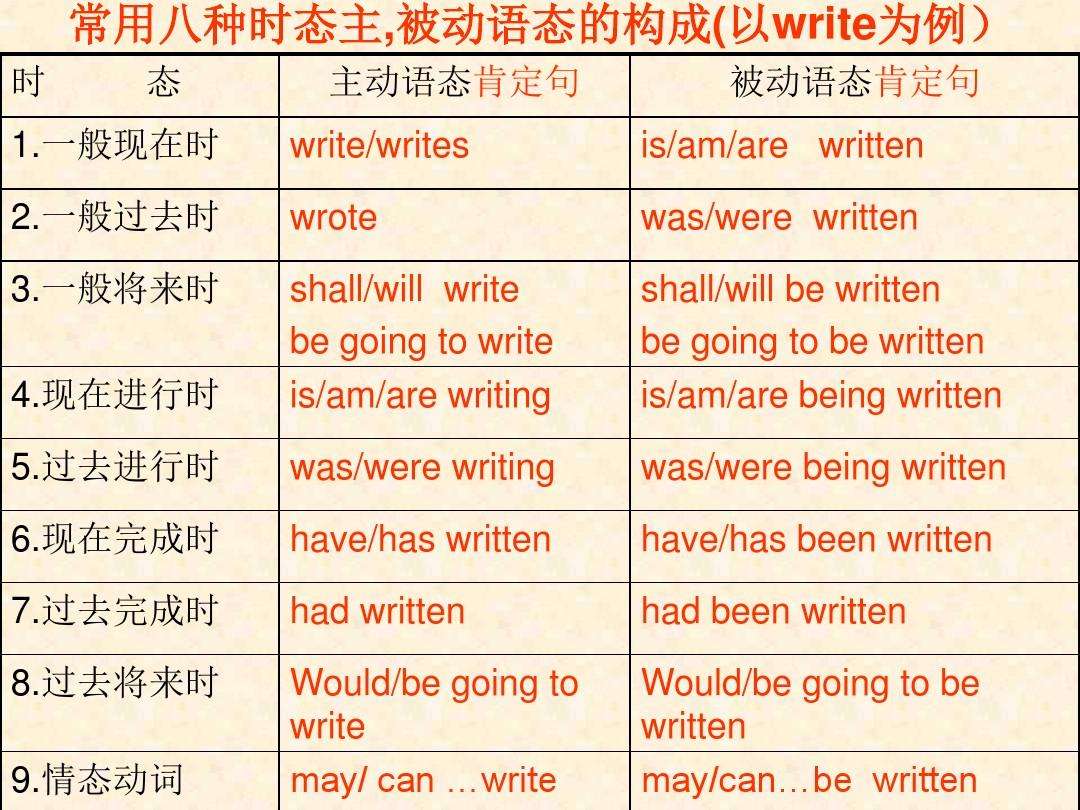
二、被动语态的构成
⑴一般现在时:do/does→be (am / is / are) done
⑵一般过去时:did→was/were done
⑶一般将来时:will /shall do→will / shall be done
⑷现在进行时:be (is/am/are)doing→be (am/is/are) being done
⑸现在完成时:have/has done→have/has been done
⑹过去进行时:was/were doing→was/were being done
⑺过去完成时:had done→had been done
⑻过去将来时:would / should do→would / should be done
⑼含情态动词:can / must /may do→can / must /may be done
注意:在进行主动语态和被动语态的互换时,时态要保持不变
三、含情态动词的被动语态
1. 其结构为“情态动词+be+过去分词”。如:
This can’t be done in a short time. 这不是短期内可以完成的。
This needn’t be mentioned in the letter. 这在信中不必提及。
2. 情态动词后的不定式可以用完成式。如:
Can this have been done by a child? 这能是一个孩子做的事吗?
The door must have been locked by Jim. 门一定是吉姆锁的。 宜城教育365速发国际靠谱么_365bet亚洲官方网址_预付365商城下载网www.bjtlcd.com |